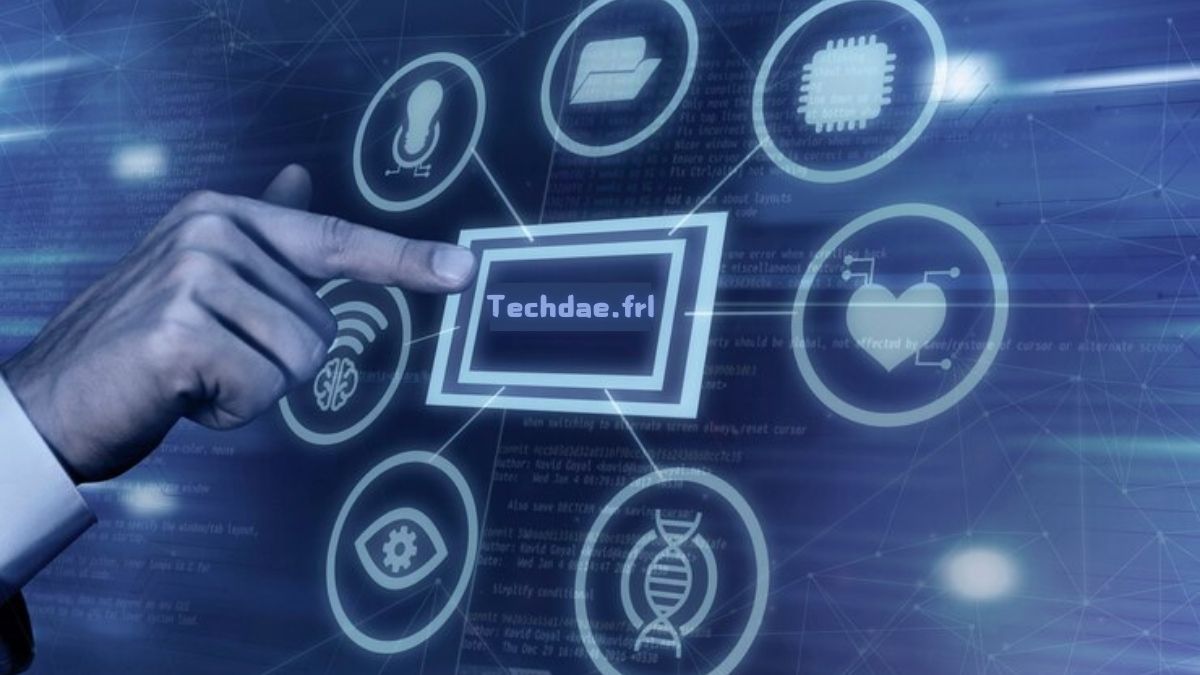
Techdae FRL is quickly becoming a beacon of innovation in the rapidly evolving world of technology. As a pioneer in multiple tech domains, Techdae FRL has redefined how industries approach technological development, from artificial intelligence (AI) to green tech solutions.
A Brief Overview
Techdae FRL, an emerging leader in the tech industry, is known for its groundbreaking contributions to various technological fields. With its headquarters nestled in a hub of innovation, Techdae FRL combines cutting-edge research with practical applications, ensuring that its products not only push boundaries but also provide real-world solutions.
Origins of Techdae FRL
Founded by a visionary group of tech enthusiasts, Techdae FRL was built on the foundation of innovation and forward-thinking. The company’s mission has always been to bridge the gap between futuristic concepts and present-day utility. From its inception, Techdae FRL has aimed to be a forerunner in technological advancements, and it has certainly lived up to that promise.
Key Innovations
The innovations spearheaded by Techdae FRL are diverse and impactful. Their advancements in AI, robotics, and sustainable tech have not only gained global recognition but also set new standards within the industry.
Techdae FRL and AI
Artificial Intelligence remains a cornerstone of Techdae FRL’s innovation portfolio. The company has developed AI systems that enhance everything from customer service chatbots to complex data analytics platforms. These systems are designed to be both intuitive and efficient, providing users with seamless experiences across various platforms.
Techdae FRL and Robotics
In the realm of robotics, Techdae FRL has broken new ground with its human-centric designs. These robots are crafted to assist in industrial settings, healthcare, and even domestic environments. Their focus is on creating machines that not only perform tasks with precision but also integrate smoothly with human operators.
Techdae FRL in Healthcare
Healthcare technology has seen a significant boost thanks to Techdae FRL’s innovative approaches. From smart diagnostic tools to robotic surgical assistants, their contributions are making healthcare more accessible and effective. These innovations are designed to reduce human error and increase the accuracy of medical procedures, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Techdae FRL in Sustainability
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, Techdae FRL is leading the charge with green tech solutions. They are developing energy-efficient systems, renewable energy technologies, and sustainable manufacturing processes. These efforts are not just about reducing carbon footprints but also about creating a sustainable future for the coming generations.
Techdae FRL and IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another domain where Techdae FRL excels. Their IoT solutions are designed to enhance connectivity and communication between devices, creating smart environments that are both efficient and user-friendly. These solutions are particularly popular in smart home technologies and industrial automation.
The Impact of Techdae FRL
Globally, Techdae FRL’s influence is unmistakable. By collaborating with international partners and investing heavily in research and development, the company has positioned itself as a key player in the global tech landscape.
Techdae FRL in Education
In the education sector, Techdae FRL has introduced platforms that make learning more interactive and engaging. By leveraging AR and VR technologies, they are transforming traditional learning into an immersive experience.
Techdae FRL’s Market Strategy
Their market strategy is as innovative as their products. By focusing on user feedback and continuously improving their offerings, Techdae FRL ensures that they remain relevant and ahead of the curve.
Techdae FRL and Cybersecurity
Understanding the importance of digital safety, Techdae FRL invests heavily in cybersecurity. Their systems are built with robust security protocols, protecting users from potential cyber threats and data breaches.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Techdae FRL’s success is partly attributed to its strategic collaborations and partnerships. By working with other tech giants and startups alike, they foster an environment of shared knowledge and innovation.
Techdae FRL in the Cloud
Cloud computing is another area where Techdae FRL has made significant strides. Their cloud solutions are known for their reliability, scalability, and security, catering to businesses of all sizes.
Future Prospects
As for what’s next, Techdae FRL is looking to expand its horizons even further. With a focus on emerging technologies like quantum computing and next-gen telecommunications, the future looks incredibly promising.
Techdae FRL’s Research
Research and development are at the heart of Techdae FRL’s operations. By continuously pushing the envelope, they ensure that their technologies remain at the forefront of innovation.
The Competitive Edge
Techdae FRL’s competitive edge lies in its commitment to quality and innovation. Unlike its competitors, it focuses on holistic solutions that address multiple facets of a problem, ensuring comprehensive results.
Challenges and Solutions
Like any other industry leader, Techdae FRL faces its share of challenges. However, their proactive approach to problem-solving ensures that they remain resilient and adaptable in a rapidly changing tech environment.
Customer Experience at Techdae FRL
Customer experience is a top priority at Techdae FRL. Their products are designed with the end-user in mind, ensuring ease of use and satisfaction.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies illustrate Techdae FRL’s success in implementing its technologies. From improving manufacturing processes to enhancing educational tools, their impact is widespread.
Techdae FRL’s Cultural Impact
Beyond technology, Techdae FRL is shaping modern digital society. Their emphasis on ethical tech development and social responsibility makes them a respected name in the industry.
Techdae FRL and Blockchain
In the blockchain space, Techdae FRL is exploring decentralized technologies that promise to revolutionize data security and transaction transparency.
Testimonials
Users from various sectors have praised Techdae FRL for its innovative solutions and customer-centric approach. These testimonials underscore the company’s commitment to excellence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Techdae FRL is not just a tech company; it’s a trailblazer shaping the future of technology. With its innovative products, strategic partnerships, and commitment to sustainability, Techdae FRL is poised to remain a dominant force in the tech industry for years to come.
FAQs
What is Techdae FRL known for?
Techdae FRL is renowned for its advancements in AI, robotics, healthcare technology, and sustainable innovations.
How does Techdae FRL contribute to sustainability?
Techdae FRL develops energy-efficient systems and renewable technologies, contributing to a greener planet.
What are the key industries Techdae FRL focuses on?
Techdae FRL focuses on multiple industries, including healthcare, education, cloud computing, and IoT.
How does Techdae FRL ensure cybersecurity?
Techdae FRL employs robust security protocols and continuously updates its systems to protect against cyber threats.
What sets Techdae FRL apart from its competitors?
Techdae FRL’s holistic approach to problem-solving and commitment to innovation give it a distinct edge over competitors.
What are Techdae FRL’s future plans?
Techdae FRL plans to expand into quantum computing and next-gen telecommunications, staying at the forefront of technological advancement.

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months ago
 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months ago
 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago
 Blog9 months ago
Blog9 months ago
 Business9 months ago
Business9 months ago
 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months ago
 Life style1 week ago
Life style1 week ago
 Blog1 week ago
Blog1 week ago



 Great for portfolio building
Great for portfolio building Limited to certain industries
Limited to certain industries